 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 11-5895-932-14&P
When the power supply is overloaded in excess of
As the core approaches saturation, it cannot carry
its rated load, a point is reached where the output
much additional magnetic flux, and the increase in
voltage drops to approximately zero. Due to the
secondary voltage is less than any proportional
magnetic shunt in the transformer, its output
increase in primary voltage. Thus, a condition of
current is limited. With excessive load current, the
relative stability of secondary voltage is reached.
effect of the ac capacitor is lost: secondary flux
Over the range of specified primary voltage, the
opposes primary flux to demagnetize the secondary
core under the secondary winding is magnetically
core leg and the output voltage collapses, limiting
saturated, and the voltage of the secondary changes
current to approximately 150 percent
short-circuit
very little for this range of primary voltage. Due to
of full load.
the magnetic shunt between the primary and
secondary windings, that part of the core under the
F-3. Maintenance
primary is not saturated
This regulated power supply is designed for
To equalize the small effect of increasing primary
continuous, unattended operation. Little or no
voltage on the secondary, a compensating coil is
maintenance is required. If due to a component
wound over the primary coil and is connected in
failure maintenance is required, be sure to shut off
series with the secondary load circuit, but out of
line voltage prior to performing any repair
phase with the secondary. Thus, when the primary
operations. Discharge any residual charge on the
voltage increases beyond the design voltage, the
dc filter capacitors by connecting a jumper across
voltage in the compensating coil also increases, but
the output terminals or across the dc capacitor
since it is out of phase with the secondary voltage,
terminals, or allow at least one minute to elapse
it subtracts from the secondary voltage an amount
after shutting off line voltage to permit the
equal to the slight increase induced in the
capacitors to discharge. The energy stored in these
secondary winding by the increase of primary
capacitors could be harmful or fatal to personnel.
voltage. Likewise, when the primary voltage
F-4. Circuit Analysis
decreases, the compensating coil voltage decreases
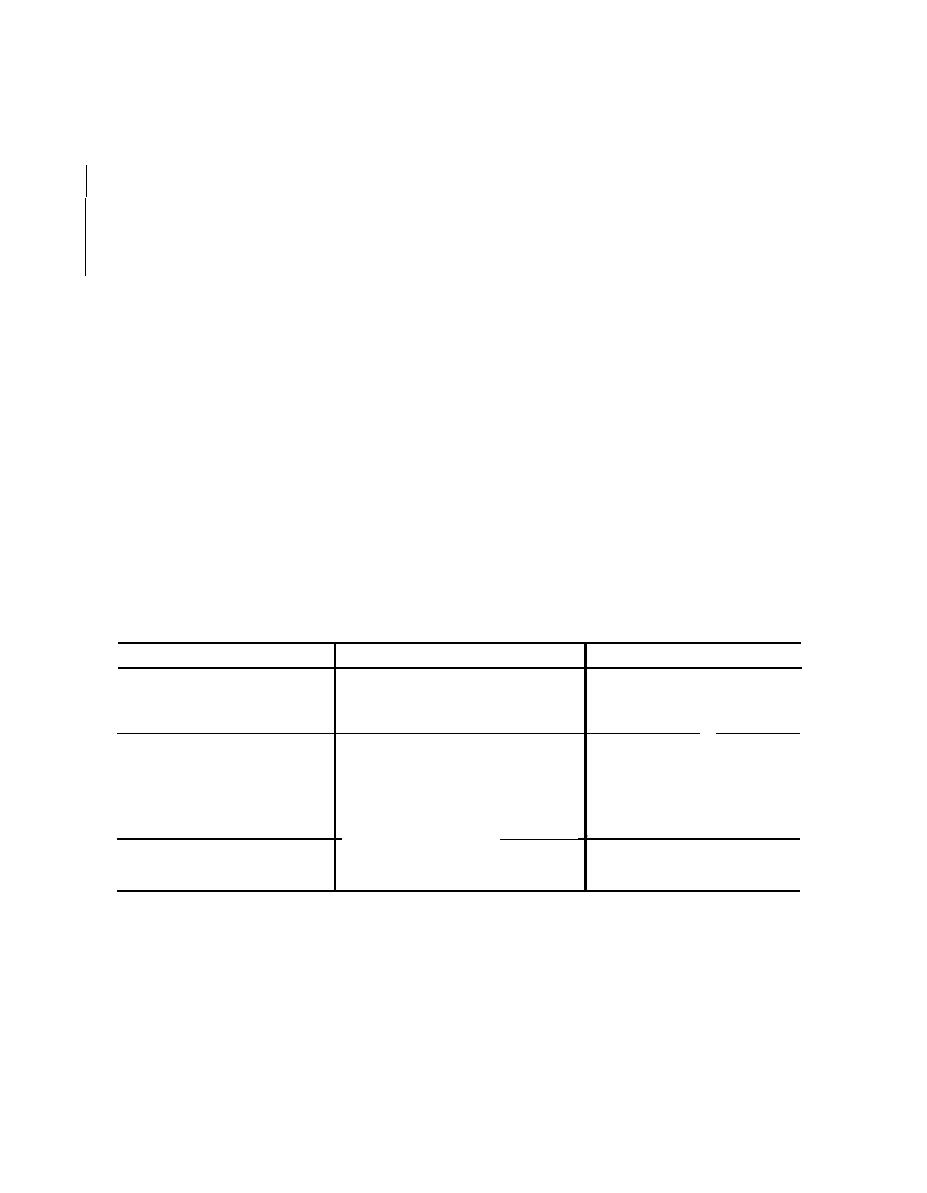
The chart below lists some possible malfunctions
in proportion to the primary voltage, and subtracts
which may be encountered in the use of the supply
from the secondary voltage. The design is such
and their corresponding cause and remedy.
that the vector sum of the compensating coil
voltage and the secondary voltage is practically
constant throughout the design range of input
voltage.
Corrective action
Probable trouble
Symptom
a Correct load current
a Load current less than minumum rated
Output voltage too high
load
b Correct primary power frequency
b Line frequency too high
a Reduce load current
Output voltage too low
a Load current greater than maximum
rated load
b Line voltage too low
b
increase primary voltage
c
Correct primary power frequency
c Line frequency too low
d Defective dc filter capacitor
d
Replace
e
Replace
e Defective ac capacitor
f
Replace
f Defective rectifier
a Check all connections and repair bad
No output voltage
a Open connection
connections
b Replace transformer
b Open transformer winding
F-3
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |